Reinforcement Learning Week 1 NPTEL Assignment Answers 2026
Need help with this week’s assignment? Get detailed and trusted solutions for Reinforcement Learning Week 1 NPTEL Assignment Answers. Our expert-curated answers help you solve your assignments faster while deepening your conceptual clarity.
✅ Subject: Reinforcement Learning
📅 Week: 1
🎯 Session: NPTEL 2025 July-October
🔗 Course Link: Click Here
🔍 Reliability: Verified and expert-reviewed answers
📌 Trusted By: 5000+ Students
For complete and in-depth solutions to all weekly assignments, check out 👉 NPTEL Reinforcement Learning Week 1 NPTEL Assignment Answers
🚀 Stay ahead in your NPTEL journey with fresh, updated solutions every week!
NPTEL Reinforcement Learning Week 1 Assignment Answers 2026
1. Which of the following is not a useful way to approach a standard multi-armed bandit problem with n arms? Assume bandits are stationary.
- “How can I ensure the best action is the one which is mostly selected as time tends to infinity?”
- “How can I ensure the total regret as time tends to infinity is minimal?”
- “How can I ensure an arm which has an expected reward within a certain threshold of the optimal arm is chosen with a probability above a certain threshold?”
- “How can I ensure that when given any 2 arms, I can select the arm with a higher expected return with a probability above a certain threshold?”
Answer : For Answers Click Here
2. What is the decay rate of the weightage given to past rewards in the computation of the Q function in the stationary and non-stationary updates in the multi-armed bandit problem?
- hyperbolic, linear
- linear, hyperbolic
- hyperbolic, exponential
- exponential, linear
Answer :
3. In the update rule Qt+1(a)←Qt(a)+α(Rt−Qt(a)), select the value of α that we would prefer to estimate Q values in a non-stationary bandit problem.
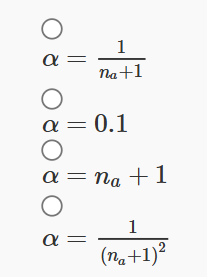
Answer :
4. Assertion: Taking exploratory actions is important for RL agents
Reason: If the rewards obtained for actions are stochastic, an action which gave a high reward once, might give lower reward next time.
- Assertion and Reason are both true and Reason is a correct explanation of Assertion
- Assertion and Reason are both true and Reason is not a correct explanation of Assertion
- Assertion is true and Reason is false
- Both Assertion and Reason are false
Answer : For Answers Click Here
5. We are trying different algorithms to find the optimal arm for a multi arm bandit. We plot expected payoff vs time graph for each algorithm for which the expected payoff satisfy some function with respect to time (staring from 0). Which among the following functions will have the least regret. (We know that the optimal expected pay off is 1)
(Hint: Plot the functions)
- tanh(t)
- 1−2−t
- x/20 if x<20 and1 after that
- Same regret for all the above functions.
Answer :
6. Consider the following statements for ϵ-greedy approach in a non-stationary environment:
i Always keeping a small constant ϵ is a good approach.
ii Large values of ϵ will lead to unnecessary exploration in the long run.
iii Decaying ϵ value is a good approach, as after reaching optimality we would like to reduce exploration.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- ii, iii
- only iii
- only ii
- i, ii
Answer :
7. Following are two ways for defining the probability of selecting an action/arm. Select the option regarding better choice among the following
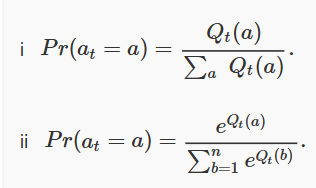
- Both are good as both formulas can bound probability in range 0 to 1.
- (i) is better because it is differentiable and requires less complex computation.
- None of the above
Answer :
8. Which of the following best refers to PAC -optimality solution to bandit problems?
ϵ – is the difference between the reward of the chosen arm and true optimal reward
δ – is the probability that chosen arm is not optimal
N – is the number of steps to reach PAC -optimality
- Given δ and ϵ, minimize the number of steps to reach PAC -optimality(i.e. N)
- Given δ and N, minimize ϵ.
- Given ϵ and N, maximize the probability of choosing optimal arm(i.e. minimize δ)
- none of the above is true about PAC -optimality
Answer :
9. Suppose we have a 10-armed bandit problem where the rewards for each of the 10 arms is deterministic and in the range (0, 10). Which among the following methods will allow us to accumulate maximum reward in the long term?
- ϵ -greedy with ϵ = 0.1.
- ϵ -greedy with ϵ = 0.01.
- greedy with initial reward estimates set to 0.
- greedy with initial reward estimates set to 10.
Answer :
10. Which of the following is/are correct and valid reasons to consider sampling actions from a softmax distribution instead of using an ϵ -greedy approach?
i Softmax exploration makes the probability of picking an action proportional to the actionvalue estimates. By doing so, it avoids wasting time exploring obviously ’bad’ actions.
ii We do not need to worry about decaying exploration slowly like we do in the ϵ-greedy case. Softmax exploration gives us asymptotic correctness even for a sharp decrease in temperature.
iii It helps us differentiate between actions with action-value estimates (Q values) that are very close to the action with maximum Q value.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- i, ii, iii
- only iii
- only i
- i, ii
- i, iii
Answer : For Answers Click Here

![[Week 1-12] NPTEL Reinforcement Learning Assignment Answers 2026](https://answergpt.in/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/NPTEL-Reinforcement-Learning-Assignment-Answers-2026.jpg)


![[Week 1-12] NPTEL Reinforcement Learning Assignment Answers 2025](https://answergpt.in/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Reinforcement-Learning.png)


![[Week 1-12] NPTEL Reinforcement Learning Assignment Answers 2024](https://answergpt.in/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/NPTEL-Reinforcement-Learning-Assignment-Answers-2024.jpg)


