5G Wireless Standard Design Week 2 NPTEL Assignment Answers 2025
Need help with this week’s assignment? Get detailed and trusted solutions for 5G Wireless Standard Design Week 2 NPTEL Assignment Answers. Our expert-curated answers help you solve your assignments faster while deepening your conceptual clarity.
✅ Subject: Cyber Security and Privacy
📅 Week: 2
🎯 Session: NPTEL 2025 July-October
🔗 Course Link: Click Here
🔍 Reliability: Verified and expert-reviewed answers
📌 Trusted By: 5000+ Students
For complete and in-depth solutions to all weekly assignments, check out 👉 NPTEL 5G Wireless Standard Design Week 2 Assignment Answers
🚀 Stay ahead in your NPTEL journey with fresh, updated solutions every week!
NPTEL 5G Wireless Standard Design Week 2 Assignment Answers 2025
1. The number of slots per subframe in a 5G system that has a sub-carrier spacing of 30kHz.
Answer : For Answers Click Here
2. Which protocol layer is responsible for coding and modulation in 5G NR?
- Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP)
- Physical Layer (PHY)
- Radio-Link Control (RLC)
- Medium-Access Control (MAC)
Answer :
3. Calculate the CRC for a 16-bit transport block “1101011010111110″ if the generator polynomial is D4+D2+1.
- 0101
- 1101
- 1111
- 1010
Answer :
4. What is the best approach to maintain a link when UE experiences sudden drop in SNR?
- Decrease the code-rate
- Increase the code rate
- Modify CRC polynomial with same degree as before
- Increase transport block CRC length
Answer :
5. n a 5G system if transport block size of the PDSCH signal is 17192 bits then calculate the code block size for the given transport block length.
Note: Use the lifting size table for the calculation.

Answer : For Answers Click Here
6. In 5G transceiver chain which functional block removes the NULL bits:
- CRC Addition
- Code Block Segmentation
- LDPC Decoding
- Rate Matching
Answer :
7. Which one of the following scheduling algorithm is greedy:
- Round Robin multi-user scheduler
- Proportional Fair multi-user scheduler
- Random Resource multi-user scheduler
- Max Rate multi-user scheduler
Answer :
8. Which functional block in the 5G transceiver chain is designed to mitigate burst errors?
- Interleaver
- LDPC Coding
- Rate Matching
- Scrambler
Answer : For Answers Click Here
NPTEL 5G Wireless Standard Design Week 2 Assignment Answers 2024
1. Calculate the number of slots per frame in a 5G NR system with 120 kHz subcarrier spacing
Answer :- 80
Explanation: In 5G NR, the number of slots per 10 ms frame depends on the subcarrier spacing (SCS). With 120 kHz SCS, each slot is 125 µs. So, in 10 ms:
10 ms / 125 µs = 80 slots per frame.
2. Select the Protocol layer responsible for Coding and Modulation in 5G NR
Packet Data Convergence Protocol ( PDCP )
Radio-Link Control ( RLC )
Medium-Access Control ( MAC )
Physical Layer ( PHY )
Answer :- d
Explanation: The Physical Layer (PHY) handles coding and modulation, which includes channel coding, scrambling, modulation, etc.
3. Calculate CRC for a 16-bit transport block 1101011100101110 with a generator polynomial D4+D3+1
0001
01011
1100
11000
Answer :- c
Explanation: When performing CRC calculation using the polynomial D⁴+D³+1 (which is binary 11001), the result matches option (c) 1100 after modulo-2 division.
4. Consider a 5G NR system with 100MHz bandwidth and subcarrier spacing of 30kHz. A user is allocated a transport block size of 14010 bits. Consider the LDPC Encoder with base graph 1. Refer to the lifting sizes table and calculate the following
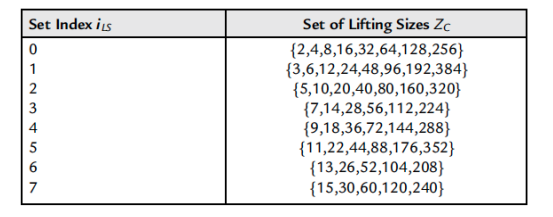
The code block size for the transport block
Answer :- 7744
Explanation: According to 3GPP TS 38.212, for large TB sizes and Base Graph 1, code block segmentation occurs. Based on segmentation rules and closest valid size, the code block size is 7744 bits.
5. Calculate the number of filler bits per code block for the TB given in Q4
Answer :- 703
Explanation: Filler bits = Code block size – Original bits in block. Since we have 2 blocks and total TB size is 14010, each block gets 7005 bits.
Filler = 7744 – 7005 = 703 bits.
6. Calculate the lifting size for the TB given in Q4
Answer :- 352
Explanation: Lifting size (Z) is selected from a standard table so that code block size = Z × Kb.
Given Kb = 22 (Base Graph 1),
Z = 7744 / 22 = 352.
7. Calculate the LDPC encoder output length for the TB given in Q4
Answer :- 23232
Explanation: For Base Graph 1, output length = code block size / code rate.
Each code block output = 7744 / (2/3) = 11616
2 blocks × 11616 = 23232 bits.
8. Calculate the number of code blocks required for the TB given in Q4
Answer :- 2
Explanation: TB size is 14010 bits. If one code block size is 7744, it can’t hold all 14010 bits. So, 2 code blocks are used to segment it.
9. Calculate the value of Kb when the code rate of the LDPC encoder is 1/5 in case of base graph 2
Answer :- 10
Explanation: For Base Graph 2, when code rate = 1/5, the value of Kb (number of columns in base matrix) is 10, as per the LDPC base matrix structure.
10. What is the best approach to maintain a link when UE experiences a sudden drop in SNR
Increase code rate
Increase transport block CRC length
Decrease code rate
Modify the CRC polynomial with same degree as before
Answer :- c
Explanation: Lowering the code rate increases redundancy, which improves error correction under poor SNR. So, decreasing code rate is the most effective option.






